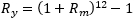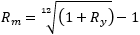Timescale consolidation methods
The following table explains timescale consolidation methods which are used to convert values between different periodicities.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Sum | When converting from smaller periodicities to larger periodicities, the values of all periods are summed up; for example, when converting from Monthly to Annually, a year will get the sum of values of all months in that year. When converting from larger periodicities to smaller periodicities, the value is divided between smaller periods; for example, when converting from Annually to Monthly, all months will get an equal share of value assigned to that year. |
| Sum – Time Weighted | When converting from smaller periodicities to larger periodicities, the values of all periods are summed up; for example, when converting from Monthly to Annually, a year will get the sum of values of all months in that year. When converting from larger periodicities to smaller periodicities, the value is divided between smaller periods weighted by the number of days in the period; for example, when converting from Annually to Monthly, each month will get a share of value assigned to that year weighted by the number of days in each month. This method is usually used for production volumes. |
| Average | When converting from smaller periodicities to larger periodicities, the values of all periods are averaged; for example, when converting from Monthly to Annually, a year will get the average of values of all the months in that year. When converting from larger periodicities to smaller periodicities, the value is assigned to all periods as it is; for example, when converting from Annually to Monthly, each month will get the same value as that assigned to that year. |
| Average – Time Weighted | When converting from smaller periodicities to larger periodicities, an average of values of all periods is calculated, weighted by number of days; for example, when converting from Monthly to Annually, a year will get the average of values of all months in that year, weighted by the number of days. When converting from larger periodicities to smaller periodicities, the value is assigned to all periods as it is; for example, when converting from Annually to Monthly, each month will get the same value as that assigned to that year. This method is usually used for production rates such as bbl/d. |
| Last Period | When converting from smaller periodicities to larger periodicities, only the value of the last period is used; for example, when converting from Monthly to Annually, a year will get the value from December of that year. When converting from larger periodicities to smaller periodicities, the value will be assigned only to the last period; for example, when converting from Annually to Monthly, December will get the value of that year and all other months will get zeros. This method is usually used for cumulative values. |
| First Period | When converting from smaller periodicities to larger periodicities, only the value of the first period is used; for example, when converting from Monthly to Annually, a year will get the value from January of that year. When converting from larger periodicities to smaller periodicities, the value will be assigned only to the first period; for example, when converting from Annually to Monthly, January will get the value of that year and all other months will get zeros. This method is usually used for opening balances. |
| Compounded |
Values are compounded using the compounding formula when converting both from smaller periodicities to larger periodicities and from larger periodicities to smaller periodicities. For example, when converting from Monthly to Annually, the following formula will be used (Ry is the annual value and Rm is the monthly value):
And when converting from Annually to Monthly, the following formula will be used:
This method is usually used for interest rates and inflation. |
| Equal Allocation Balance | When converting from smaller periodicities to larger periodicities, the value of the last period is used; for example, when converting from Monthly to Annually, a year will get the value from December of that year. When converting from larger periodicities to smaller periodicities, the value is assigned to all periods as it is; for example, when converting from Annually to Monthly, each month will get the same value as that assigned to that year. |